Mechanisms of Melanin Suppression and Spot Prevention by Pineapple Ceramide
Mechanisms of Melanin Suppression and Spot Prevention by Pineapple Ceramide
Preventing dark spots and freckles caused by melanin is one of the major beauty concerns for many people. In recent years, various ingredients have been reported to have such effects, and among them, ceramides derived from pineapple have been attracting growing attention.
In this column, we will discuss the potential of pineapple ceramide to suppress melanin production, based on medical evidence, and provide a detailed explanation of the mechanisms by which it may contribute to the prevention of dark spots.

What is Pineapple Ceramide?
Pineapple ceramide is an ingredient extracted from pineapple fruit, and it is believed to mainly contribute to moisturizing and strengthening the skin’s barrier function.
Ceramides are a type of lipid found in the stratum corneum of the skin, playing an essential role in skin protection and hydration. Pineapple ceramide is one such ingredient with these properties and is widely used in cosmetic products.
Scientific Evidence of Its Effects
Inhibition of Melanin Production: Several studies have reported on the effects of pineapple ceramide on melanin production. Melanin is a major pigment in the skin and contributes to the formation of dark spots and dullness; therefore, suppressing its production is considered beneficial for skin brightening and improving pigmentation.
Antioxidant Effects: Pineapple ceramide has been reported to help alleviate oxidative stress in the skin. Oxidative stress refers to the burden placed on cells by ultraviolet radiation and other external stimuli, and it is one of the factors that can enhance melanin production, leading to dark spots. Therefore, reducing oxidative stress may help regulate melanin levels. In fact, ingredients that mitigate cellular damage are recognized as important supportive components for preventing dark spots and pigmentation.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Pineapple ceramide has also been reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory activity. Inflammatory responses can activate melanocytes and promote melanin production; therefore, suppressing inflammation may contribute to the prevention of pigmentation. In this way, the anti-inflammatory effect is considered one of the key mechanisms by which pineapple ceramide regulates skin pigmentation.
Mechanisms of Action of Pineapple Ceramide
Enhancement of Skin Barrier Function: Ceramides are a major lipid component present in the stratum corneum, playing an essential role in maintaining the skin barrier. By strengthening this barrier, the impact of external stimuli and ultraviolet (UV) radiation can be mitigated, potentially suppressing UV-induced melanin production. This barrier-enhancing effect is considered a fundamental mechanism that forms the basis for various skin-protective effects, including skin brightening.
Improvement of Moisture Retention: Ceramides also play a role in maintaining water content within the skin, and a deficiency can lead to dryness and disruption of the stratum corneum. Since dryness is considered a factor that promotes melanin production, maintaining adequate hydration directly contributes to the prevention of pigmentation. Supplementation with pineapple-derived ceramides may enhance the skin’s moisture retention capacity, potentially leading to an indirect suppression of melanin synthesis.
Collagen Production–Promoting Potential: Some basic research suggests that ceramides may act on skin fibroblasts to promote collagen synthesis. Collagen is a key component that supports the dermal structure and is essential for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity. Although this is not a direct whitening effect, by maintaining overall skin health, it is expected to complement the suppression of excessive melanin production. However, clinical evidence in humans is still limited, and further studies are needed to validate this effect.
Support of Skin Turnover by Bromelain (Proteolytic Enzyme)
Bromelain is a proteolytic enzyme found in the fruit and stem of pineapple. While it is primarily known for its role as a digestive enzyme, it is also expected to have beneficial effects in skincare by gently breaking down aged keratin and supporting the natural skin turnover process.
When skin turnover functions properly, old cells containing melanin are more efficiently shed, which may help prevent dark spots and dullness. In addition, bromelain is reported to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe skin irritation caused by external stimuli.
Improvement of Intestinal Environment and Prevention of Skin Problems through Dietary Fiber
Another component worth highlighting is the dietary fiber found in pineapple. The gut and skin are closely connected, and when beneficial gut bacteria are activated, bowel movements become regular, helping to eliminate accumulated waste and toxins from the body. This, in turn, can reduce the risk of skin problems such as acne and irritation.
Pineapple contains both soluble and insoluble dietary fibers, providing balanced support for gut health. As an inner-care approach that starts from the gut, dietary fiber is essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin.
Expected Synergistic Effects of Ceramides and Supporting Ingredients
In this way, pineapple contains not only ceramides but also supporting compounds that help regulate skin metabolism and gut health. Bromelain promotes skin surface turnover, while dietary fiber helps maintain internal balance, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of ceramides.
Pineapple can truly be considered a comprehensive cosmetic fruit, offering multiple beauty benefits such as moisturizing, strengthening the skin barrier, promoting skin turnover, and improving gut health.
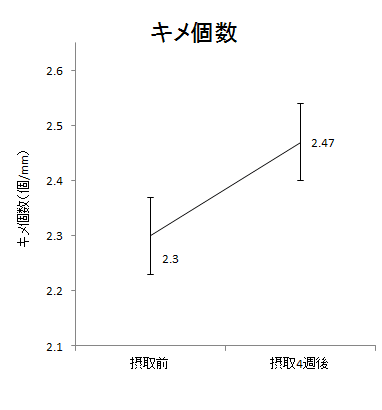
Results from Research and Clinical Trials
Some studies have indicated that the use of skincare products containing pineapple ceramide can contribute to the improvement of uneven skin tone and dark spots.
For example, in certain clinical trials, participants who used products containing pineapple ceramide over a specified period reported an improvement in skin brightness.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Pineapple ceramide is an ingredient expected to provide multifaceted skin benefits, including moisturizing, strengthening the skin barrier, and suppressing melanin production. Synergistic effects may also be achieved when combined with supporting ingredients such as bromelain and dietary fiber.
Going forward, further clinical trials and studies on its combined effects with other compounds are expected to provide additional evidence of its efficacy.
Supervisor

- President
- Born in Gunma Prefecture in 1965, he completed his doctoral studies at the Graduate School of Agricultural Science at Tokyo University of Agriculture (PhD), and served as a special research fellow at the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, a part-time lecturer at Tokyo University of Agriculture, and an associate professor and professor at Takasaki University of Health and Welfare before becoming a professor at Tokyo University of Agriculture in April 2012. He is a professor at the same graduate school, and will be the president of Tokyo University of Agriculture in April 2021. He will be the chairman of Tokyo University of Agriculture in July 2023.
School he attended
April 1984 - March 1988 Graduated from the Department of Forestry (Forestry Science Course), Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture
Degrees he received
Tokyo University of Agriculture - Doctor of Forestry
Career history within the university
April 2012 - Ongoing Professor, Department of Forest Science, Faculty of Regional Environmental Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture
April 2016 - Ongoing Director, Food and Agriculture Museum, Tokyo University of Agriculture (Other organizations)
April 2021 - Ongoing President, Tokyo University of Agriculture
Academic societies and committees he has been affiliated with
April 1985 - Ongoing Japan Wood Research Society
June 1988 - Ongoing Japanese Mushroom Society
April 1995 - Ongoing Japanese Society of Inflammatory and Regenerative Medicine
April 1995 - Ongoing Japanese Society of Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agricultural Chemistry
May 1995 - Ongoing Applied Pharmacology Research Society
Latest Posts
- February 19, 2026 Functionality of pineapple ceramide The dullness-improving effect of pineapple-derived glucosylceramide
- January 29, 2026 Functionality of pineapple ceramide Melanin Production-Inhibiting Effects of Phytol in Brightening Pine
- December 29, 2025 Functionality of pineapple ceramide Clinical trial: Effects on Skin Brightness
- November 27, 2025 Functionality of pineapple ceramide Clinical trial: Effects on moisturizing efficacy
- October 30, 2025 Functionality of pineapple ceramide Pineapple Cultivation and Nutritional Value